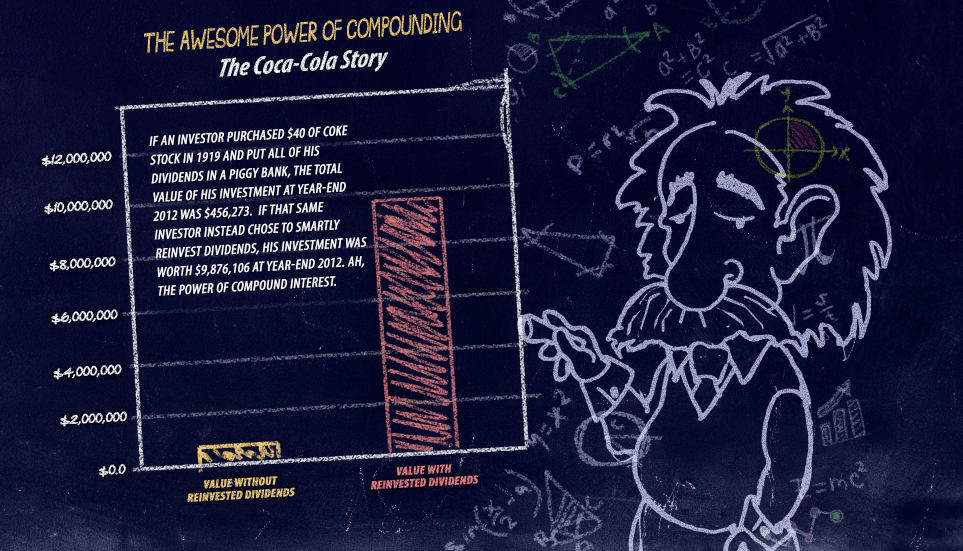
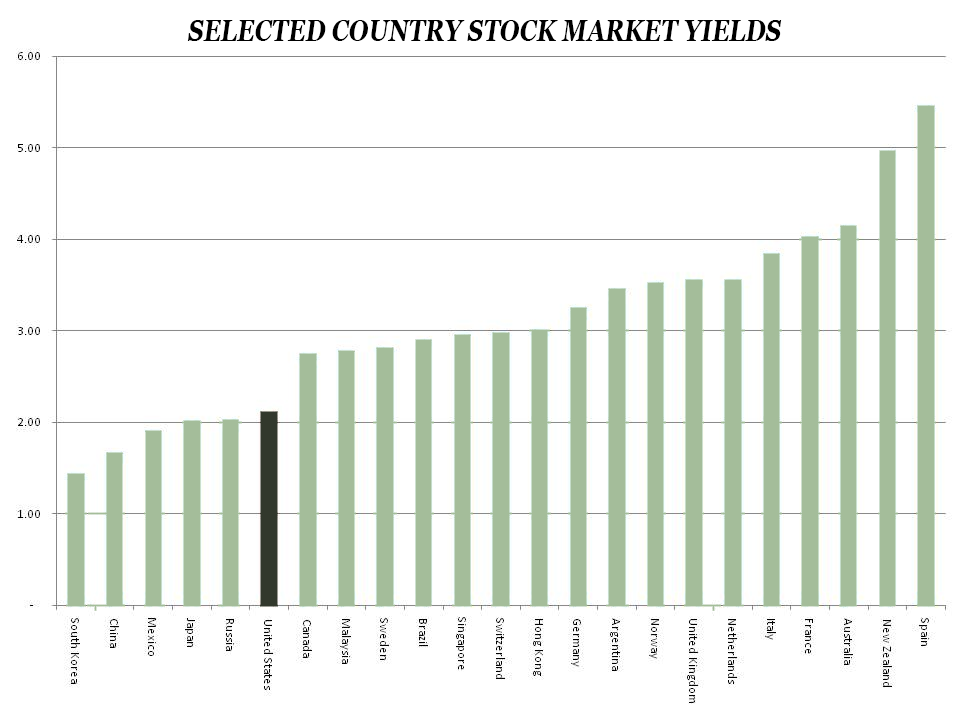
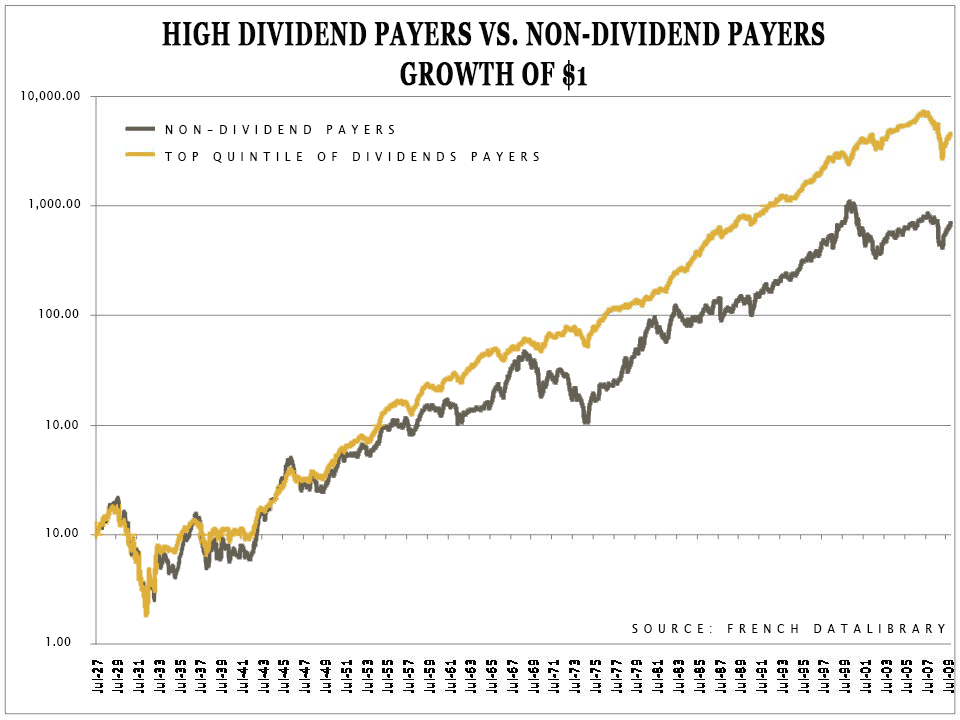
Why are dividends important? Because they allow the power of compound interest to work for you. I was speaking with a client yesterday who is in the process of helping his children establish Roth IRAs. I told him it’s amazing how just getting in the game can do wonders for one’s financial well-being: Imagine what this will look like in 50-years. Remember, just the process of starting an investment puts you or a loved one light years ahead of those bogged down and doing nothing at all.
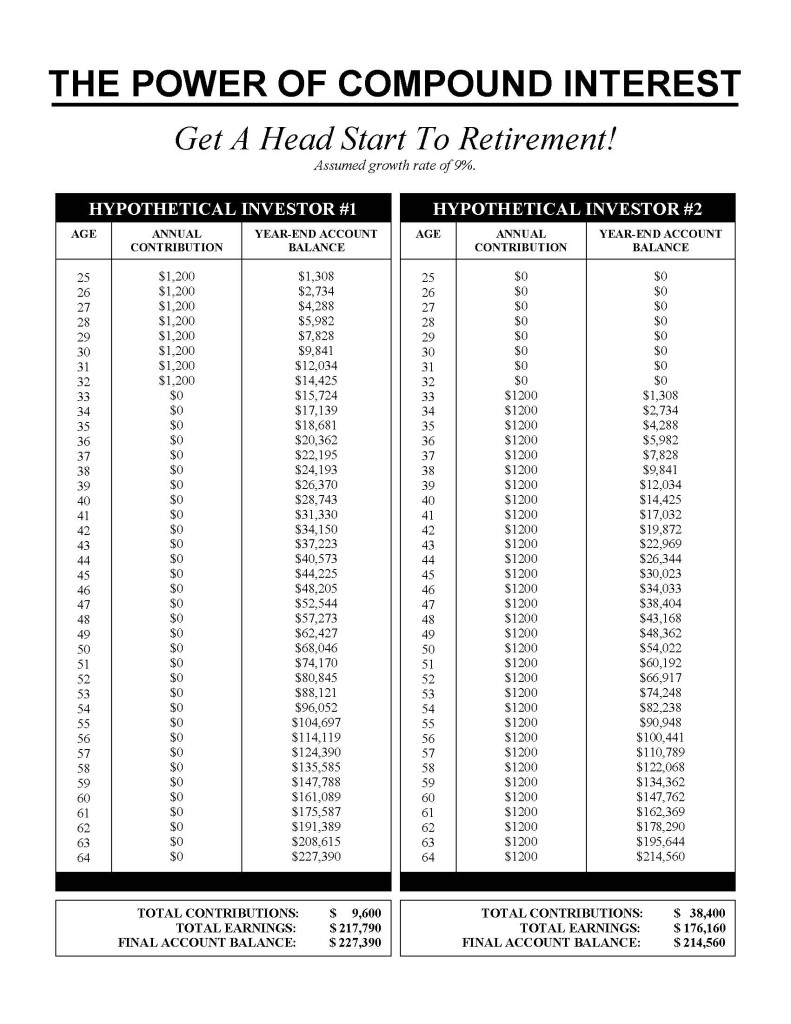
Take a look below at the power of compound interest. An investor who makes eight annual contributions starting at age 25 and then makes no more will end up at age 64 with $227,390 at an assumed growth rate of 9%. Meanwhile, another investor who skips those eight contributions early in life and begins investing later at 33 and makes annual contributions each year until age 64 will end up with only $214,560 that year (assuming the same 9% growth rate). That’s the power of compounding.
Originally posted March 24, 2017.